Is A Drone A Robot? Yes and No. If the drone act like a robot, then it is a robot. For this, it needs to be autonomous and have to do the task they were to perform. However, most drones are operated by users and are not fully automated. So, in those cases, we will not call those drones robots.
Probably one of the best examples of robotic drones is the drones used for agriculture. Those drones are automated and do specific tasks.
What is Drone?
A drone, also known as an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), is an aircraft that is piloted remotely or flies autonomously without a human onboard.
Unmanned aerial vehicles or Drones come in various sizes, shapes, and designs, ranging from small quadcopters to large fixed-wing aircraft. They are equipped with sensors, cameras, and other electronic systems that allow them to collect data, navigate, and perform tasks.
Drones have been around for decades, but their popularity has surged in recent years, driven by technological advancements and the availability of affordable and user-friendly models.
Today, drones are used in a wide range of applications, from military drones to commercial photography, agriculture, search and rescue operations drones are being used for a wide range of applications..
One of the main advantages of drones is their ability to access areas that are difficult or impossible for humans to reach. For example, they can fly over rugged terrain, survey crops from above, inspect buildings, and even explore the depths of the ocean.
Drones can also be used to monitor wildlife and track their movements, providing valuable data for conservation efforts.
Another benefit of drones is their cost-effectiveness and efficiency. Compared to traditional unmanned aircraft or ground-based methods, drones are much cheaper to operate and can cover larger areas in less time.
For example, in agriculture, drones equipped with specialized cameras can capture high-resolution images of crops, enabling farmers to detect crop stress, disease, or irrigation issues before they become more severe and costly to address.
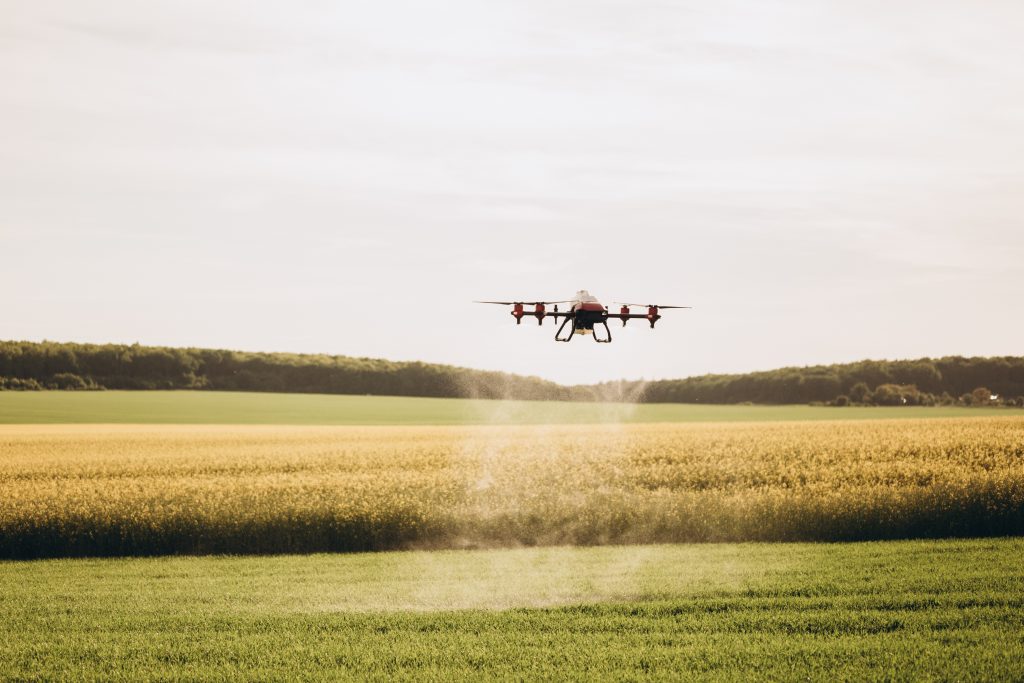

What is Robot?
A robot is a machine that is designed to perform tasks automatically or with minimal human intervention.
Robots can come in various shapes and sizes, from humanoid robots that resemble humans in appearance and movement to industrial robots that are used in manufacturing and assembly lines to social robots that can interact with humans and provide emotional support.
Robots can also be used in a wide range of applications, from transportation to exploration, to entertainment, to caregiving.
For example, autonomous vehicles are being developed to transport goods and people safely and efficiently, while space robots are being used to explore other planets and gather data for scientific research.
Another benefit of robots is their adaptability and ability to learn from experience.
With advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning, robots can be trained to perform a wide range of tasks and to adapt to new situations and environments. This has the potential to transform industries and create new opportunities for innovation and growth.
However, the increasing use of robots also raises concerns about their impact on jobs, privacy, and security. As robots become more advanced and capable of performing tasks traditionally done by humans, there is a risk of job displacement and economic inequality.
Additionally, the collection and use of data by robots can raise privacy and security concerns, requiring careful regulation and ethical considerations.
Similarities Between Drones and Robots
So How closely is drone technology related to robotics technology?
Well, Drones and robots have some similarities in terms of their design, purpose, and capabilities. Here are some of the key similarities:
Sensors and computing systems
Both drones and robots use sensors, cameras, and other electronic systems to navigate, detect objects, and collect data. These systems can range from simple obstacle detection sensors to advanced computer vision systems that enable them to recognize and interpret complex environments.
Remote or autonomous operation
Both drones and robots can be operated remotely by a human operator using a remote control or a computer interface. They can also be programmed to perform tasks autonomously without the need for human intervention.
Potential to revolutionize industries
Both drones and robots have the potential to transform various industries by enabling new applications and increasing efficiency. For example, drones can be used in agriculture to monitor crops and optimize irrigation, while robots can be used in manufacturing to increase productivity and reduce costs.
Use of Advanced Technologies
Both drones and robots rely on advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and computer vision to perform tasks more effectively and efficiently. These technologies enable them to learn from experience and adapt to changing environments, making them more versatile and flexible.
Multidisciplinary approach
Both drones and robots require expertise in various fields, such as mechanical engineering, electronics, computer science, and control systems.
This multidisciplinary approach is necessary to design, build, and operate these complex machines.
Customization and adaptability
Both drones and robots can be customized and adapted to specific tasks or environments.
For example, drones can be equipped with different cameras or sensors depending on the application, while robots can be designed with different end-effectors for specific tasks such as welding or painting.
Mobility and Agility
Both drones and robots are designed to be mobile and agile, enabling them to move through different environments and navigate obstacles.
Drones can fly through the air and avoid obstacles using sensors and GPS, while robots can move on wheels, legs, or tracks and climb stairs or navigate rough terrain.
Interdisciplinary Applications
Both drones and robots have a wide range of interdisciplinary applications that span various fields, such as agriculture, construction, healthcare, and entertainment. For example, drones can be used in search and rescue missions, while robots can be used in surgery or physical therapy.
Ethical considerations
Both drones and robots raise ethical considerations related to privacy, safety, and security.
For example, drones may be used for surveillance or monitoring activities that violate privacy, while robots may pose safety risks if they malfunction or are used inappropriately.
As such, it is important to ensure that these technologies are used ethically and responsibly.
In conclusion, while drones and robots have different designs and purposes, they share some similarities in their use of sensors and computing systems, remote or autonomous operation, potential to revolutionize industries, use of advanced technologies, and multidisciplinary approach.
Understanding these similarities can help us appreciate the value and potential of these technologies and inspire further innovation in the field.
Differences between drones and robots
Drones and robots have different designs, purposes, and capabilities, which result in some key differences between them. Here are some of the main differences:
Mobility
Drones are designed for aerial mobility, while robots can move on land, water, or air. Drones rely on rotors or propellers to generate lift and move through the air, while robots use wheels, legs, or tracks to move on the ground.
Purpose
Drones are typically used for surveillance, mapping, inspection, or delivery, while robots are used for tasks such as manufacturing, assembly, welding, or cleaning. Drones are often used in outdoor environments, while robots are used in indoor environments.
Payload capacity
Drones are generally designed to carry lightweight payloads such as cameras or sensors, while robots can carry heavier payloads such as tools or equipment. This is because drones require more energy to stay airborne and have limited carrying capacity.
Sensing and perception

Drones are equipped with sensors such as cameras or lidar to navigate and detect objects, while robots use sensors such as proximity sensors or force sensors to perform tasks.
Drones rely on vision-based sensing to detect obstacles and navigate, while robots may rely on tactile sensing or force sensing to manipulate objects.
Control and autonomy
Drones are often operated remotely by a human operator, while robots can be programmed to perform tasks autonomously. Drones may have limited autonomy features such as obstacle avoidance or auto-landing, but they still require a human operator to oversee the operation. Robots, on the other hand, can be programmed to perform tasks without human intervention.
Design and construction
Drones are typically constructed using lightweight materials such as plastic or carbon fiber to minimize weight and maximize flight time. Robots may have more complex designs and may require heavy-duty materials such as steel or aluminum to withstand the forces involved in their tasks.
Here is a table summarizing some of the key differences between drones and robots:
| Feature | Drones | Robots |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility | Designed for aerial use | Can move on land, water, or air |
| Purpose | Surveillance, mapping, etc. | Manufacturing, assembly, etc. |
| Payload capacity | Carries lightweight loads | Can carry heavy payloads |
| Sensing and perception | Vision-based sensing | Tactile or force-based sensing |
| Control and autonomy | Human-operated or limited autonomy | Can be programmed to perform tasks autonomously |
| Design and construction | Lightweight materials | Complex designs and heavy-duty materials |
| Power source | Powered by batteries | May use electricity, hydraulic systems, or combustion engines |
There are other differences like a drone is an unmanned vehicle. However, this is changing in some cases after the Jetson human flying drone. So, there are like two types of drones, one in the autonomous category and the other in the opposite category or, say, the normal ones.
Autonomous drones can be called flying robots, while normal drones are not.
Let’s see the main differences between autonomous drones and normal drones.
Autonomous Drones vs Normal Drones

| Feature | Autonomous Drones | Normal Drones |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Operate autonomously without human control | Controlled by a human operator |
| Navigation | Use advanced algorithms and sensors to navigate and avoid obstacles | Require constant input from a human operator to navigate |
| Mission planning | Can plan and execute missions on their own | Require a human operator to plan and execute missions |
| Efficiency | Can operate for extended periods of time and cover large areas | Limited flight time and range due to human fatigue and limitations |
| Safety | Can avoid obstacles and respond to emergencies on their own | May crash or get lost due to human error or mechanical failure |
| Complexity | Require advanced software and hardware | Simpler design and technology |
| Cost | Can be more expensive due to advanced technology | Can be more affordable for basic applications |
| Applications | Ideal for applications such as mapping, surveying, delivery, and inspection | Used for a variety of applications but may not be suitable for complex or long-range missions |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the question of whether a drone is a robot is complex and nuanced. While there are similarities between drones and robots, such as their use of sensors and computing systems, there are also significant differences in their design, purpose, and capabilities.
A Drone has an unmanned aerial system and is typically designed for aerial use, while a robot can operate on land, water, or air, depending on how it was made.
Drones are often used for applications such as surveillance, mapping, and delivery, while robots are used for manufacturing, assembly, and other complex tasks.
Furthermore, while some drones can operate autonomously, they often require a human operator for navigation and control.
On the other hand, robots can be programmed to perform tasks autonomously without human intervention.
Despite these differences, the technologies behind both drones and robots are rapidly advancing, with the potential to revolutionize various industries and improve efficiency and safety in a variety of applications.
Overall, the distinction between drones and robots is not always clear-cut, and the terms are often used interchangeably in popular culture.
However, it is important to understand the differences between the two and appreciate their unique capabilities and limitations.
As both technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and exciting applications of drones and robots in the future.
So, when a drone has similarities to a robot, we can say that a drone is a flying robot.

